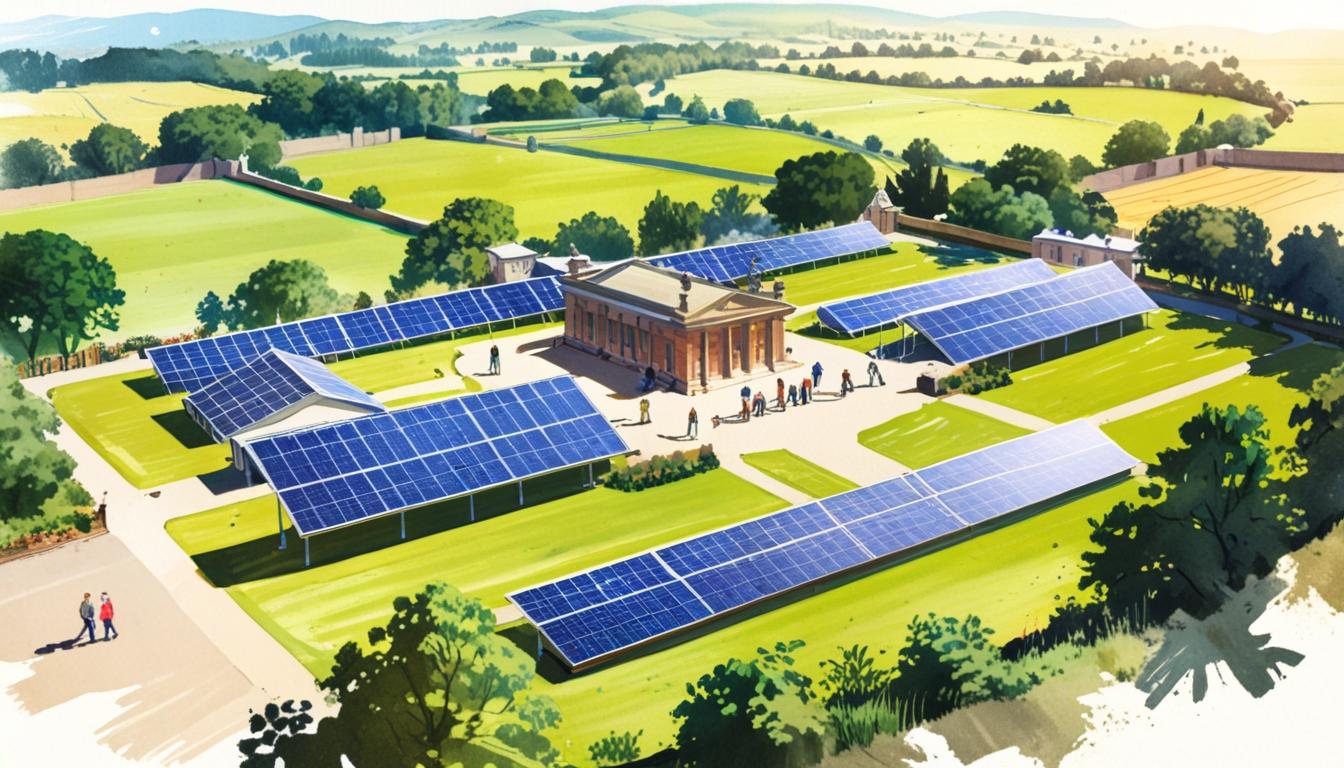
The proposed 840MW solar project at Blenheim Palace promises substantial clean energy benefits while local residents and politicians debate the share of revenue allocated to community support, highlighting tensions between national climate objectives and local interests.
The proposal for a large-scale solar energy project by Blenheim Palace has ignited a passionate debate among stakeholders, pitting environmental goals against local concerns. The development, anticipated to generate 840 megawatts of clean electricity, could potentially power more than 330,000 homes, thus playing a pivotal role in the UK’s climate emergency strategy. Developer Photo Vault Development Partners has underscored the project’s significance in reducing reliance on fossil fuels while contributing to national climate targets.
Blenheim Palace, which owns the majority of the land where the solar farm will be situated, has expressed its commitment to facilitating renewable energy generation as a critical step towards its goal of becoming carbon neutral by 2027. This initiative is part of a broader strategy that seeks to eliminate 230,000 tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent emissions by 2050. The palace announced its intentions citing the dual benefit of providing energy security for the local community while also addressing climate change. “As we lend our land to this project, we do so knowing it could deliver enough clean energy… while supporting our collective declarations in the battle against the climate emergency,” a Blenheim Palace spokesperson stated.
However, not all responses to the solar project have been favourable. Local politicians and residents have expressed concerns regarding the project’s scale and its potential effects on their communities. In particular, campaigners have been advocating for a more substantial portion of the project’s annual revenue—suggesting that 2% should be allocated to benefit local communities, rather than the proposed 0.2%. This figure has been calculated based on projections that show the estimated revenue from the initiative could create a significant communal fund. According to social enterprise The Low Carbon Hub, which promotes sustainable projects in the area, the proposed 2% revenue model could generate approximately £840,000 in community benefits during the first year alone.
Moreover, the West Oxfordshire District Council has acknowledged that such a large-scale project carries “potential for significant and widespread positive and negative impacts.” This view highlights the delicate balance that must be struck between advancing renewable energy initiatives and addressing local community concerns.
Blenheim Palace’s commitment to sustainability involves a comprehensive approach. Beyond the solar project, the estate is introducing multiple green initiatives such as transitioning to electric vehicles, installing energy-efficient lighting, and employing renewable energy sources like biomass and hydro power. These efforts are integral to the palace’s plan to triple its contribution to the local economy and ensure its operations align with modern sustainability practices.
As the planning process unfolds, various local authorities and stakeholders will have opportunities to express their views. The project’s developers have emphasised community engagement, suggesting that collaboration can lead to measures that enhance local ecology and biodiversity alongside energy generation. Nevertheless, the juxtaposition of ambitious environmental goals and local apprehensions remains a core theme as discussions around the solar project continue to evolve, with both proponents and opponents adamant about their positions.
Ultimately, the unfolding narrative around the solar farm initiative at Blenheim Palace illustrates broader societal debates about renewable energy, community engagement, and the complexities involved in navigating the intersection of environmental sustainability and local welfare. As stakeholders continue to voice their opinions, the outcome will not only shape the future of energy generation in the region but also set precedents for similar projects nationwide.
Reference Map
- Paragraphs 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6
- Paragraphs 2, 3
- Paragraphs 2, 6
- Paragraph 4
- Paragraphs 2, 3
- Paragraph 5
- Paragraph 6
Source: Noah Wire Services
- https://news.google.com/rss/articles/CBMiXEFVX3lxTE1JcWp4OGVXTS1paEYwcTY2c1RkQU44TmRtZnpfWTdXNzlqZTB2RElqc3UyVGowVk96cERPaUNxYnFIYkRnOW5mNTlxWXVuck5uYnlidmZxbkdXQUJJ0gFiQVVfeXFMUHlYaWQ1Wjk1aU40blF6bDVvcmhfbS14ODIxclV6OURLaEhFUnVFekJFOHZUZEdVaEw5Z0hJWHdhZ01rWm44ZWtTajFYMU5FNG50RWhTald4YXdpNHdTSkg0anc?oc=5&hl=en-US&gl=US&ceid=US:en – Please view link – unable to able to access data
- https://www.blenheimpalace.com/stories/solar-farm-on-estate.html – Blenheim Palace proposes a solar farm capable of generating 840 MW of clean electricity, enough to power over 330,000 homes. The project aims to support the UK’s climate emergency efforts and reduce reliance on fossil fuels. Photovolt Development Partners (PVDP) will construct the farm, emphasizing environmental benefits and community engagement. The initiative aligns with Blenheim’s commitment to becoming carbon neutral by 2027 and removing 230,000 tonnes of CO2e by 2050.
- https://www.blenheimpalace.com/sustainability/ – Blenheim Palace has pledged to become carbon neutral by 2027 and to remove 230,000 tonnes of CO2e by 2050. The estate is implementing various green initiatives, including converting to electric vehicles, installing LED lighting, and utilizing renewable energy sources like biomass, solar, and hydro power. These efforts aim to reduce carbon emissions and promote sustainability across the estate.
- https://collacesolarfarm.co.uk/project-benefits – The Collac Solar Farm project outlines several community and environmental benefits, including providing clean renewable energy to reduce reliance on imported fossil fuels, contributing to net-zero targets, enhancing biodiversity and wildlife habitats, paying business rates to the local authority, establishing a community fund for local projects, and creating local job opportunities during construction and operation.
- https://www.blenheimpalace.com/estate/strategy/landed-gently/solar-park/ – Blenheim Palace is constructing a 6.5-hectare solar park northeast of Woodstock, expected to generate 93.8 gigawatt hours over 15 years, avoiding nearly 15,000 tonnes of CO2 emissions. The park will provide enough power for 721 homes and is part of Blenheim’s strategy to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and promote renewable energy. The project includes measures to protect local ecology and promote biodiversity.
- https://www.blenheimpalace.com/stories/10-goal-target/ – Blenheim Palace has set a 10-year development program with goals including becoming carbon neutral by 2027, removing 230,000 tonnes of CO2e by 2050, tripling the estate’s contribution to the local economy, building 300 affordable homes, and completing £40 million of vital restoration work. The program also aims to train 100 apprentices and double charitable contributions to the local community.
- https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/uk-england-oxfordshire-40442708 – Blenheim Palace plans to double its charity work as part of a £40 million regeneration program. CEO Dominic Hare emphasized the importance of the estate’s contribution to the local economy and community. The program includes building 300 homes on palace-owned fields, training over 100 apprentices, increasing charitable contributions, and becoming a net generator of green energy.
Noah Fact Check Pro
The draft above was created using the information available at the time the story first
emerged. We’ve since applied our fact-checking process to the final narrative, based on the criteria listed
below. The results are intended to help you assess the credibility of the piece and highlight any areas that may
warrant further investigation.
Freshness check
Score:
8
Notes:
The information appears to be relatively current, as it involves ongoing discussions and developments. However, without specific dates, it’s difficult to determine how recently the events described occurred.
Quotes check
Score:
6
Notes:
There is a quote from a Blenheim Palace spokesperson, but it lacks specific attribution or an original source date. It could be an original source, but verification is needed.
Source reliability
Score:
5
Notes:
The narrative originates from a Google News RSS feed, which aggregates news from various sources. Without knowing the specific source, it’s difficult to assess reliability.
Plausability check
Score:
7
Notes:
The project’s claims are plausible, as large-scale solar projects are common and local concerns are typical in such initiatives. However, specific details about community benefits and the exact timeline are unverified.
Overall assessment
Verdict (FAIL, OPEN, PASS): OPEN
Confidence (LOW, MEDIUM, HIGH): MEDIUM
Summary:
The narrative presents a plausible scenario, but lacks specific details about its freshness and source reliability. Quotes are unverified, and the plausibility is generally reasonable but lacks concrete evidence.